Capacitance:
The capacitance of capacitor is expressed as AC capacitance by
measuring impedance and separating factors. Also, the AC
capacitance depends upon frequency, voltage and other
measuring methods. In fact, JIS C 5101 prescribes that the series
capacitive factor of an equivalent series ( )
circuit shall be the capacitance measured at a frequency of
120 Hz and applying a maximum AC voltage of 0.5Vrms with
a DC bias voltage of 1.5 or 2.0 V to aluminum electrolytic
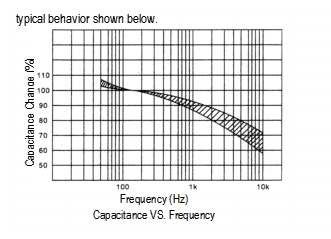
capacitors. The capacitance of an aluminum electrolytic
capacitor becomes smaller with increasing frequency. See the
typical behavior shown below.
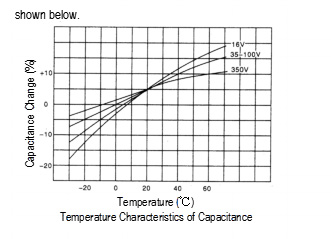
The capacitance value is highly dependent upon temperature
and frequency. As the temperature decreases, the capacitance
becomes smaller. See the typical behavior
shown below.
On the other hand, DC capacitance, which can be measured by
applying a DC voltage, shows a slightly larger value than the AC
capacitance at a normal temperature and has the flatter
characteristic over the temperature range.
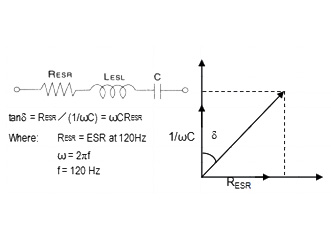
tanδ (tangent of loss angle or dissipation factor)
The tanδ is expressed as the ratio of the resistive component
(RESR) to the capacitive reactance (1/ωC) in the equivalent series
circuit . Its measuring conditions are the same as the capacitance.
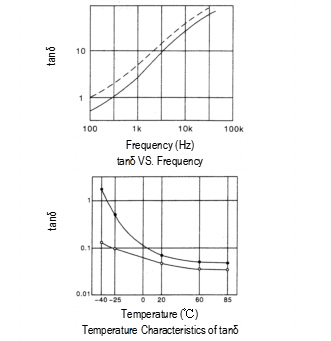
The tanδ shows higher value as the measured frequency
increases and the measured temperature decreases.
Equivalent series resistance (ESR):
The ESR is the series resistance consisting of the aluminum
oxide layer, electrolyte/separator combination and other
resistance related factors, foil length. Foil surface area and
others.
The ESR value depends upon the temperature. Decreasing
the temperature makes the resistivity of the electrolyte increase
and leads to increasing ESR.
As the measuring frequency increases, the ESR decreases
and reaches an almost constant value that mainly dominates
the frequency-independent resistance relating electrolyte/
separator combination.
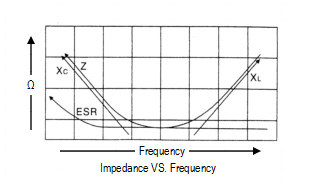
Impedance (Z):
The impedance is the resistance of the alternating current at
a specific frequency. It is related to capacitance [C] and
inductance [L] in terms of capacitive and inductive reactance,
and also related to the ESR. It is expressed as following:
Z = √[ESR2 + (XL - XC)2]
Where:
XC = 1/ωC = 1/2πfC
XL = ωL = 2πfL
As shown below, the capacitive reactance (XC) dominates at
the range of low frequencies, and the impedance decreases
with increasing frequency until it reaches the ESR in the
middle frequency range. At the range of the higher frequencies
the inductive reactance (XL) comes to dominate, so that the
impedance increases when increasing the measuring frequency.